Developing sites that are fast everywhere can be a tricky prospect. The plethora of device capabilities—and the quality of the networks they connect to—can make it seem like an insurmountable task. While we can take advantage of browser features to improve loading performance, how do we know what the user’s device is capable of, or the quality of their network connection? The solution is client hints!
Client hints are a set of opt-in HTTP request headers that give us insight into these aspects of the user’s device and the network they’re connected to. By tapping into this information server side, we can change how we deliver content based on device and/or network conditions. This can help us to create more inclusive user experiences.
It’s All About Content Negotiation
Client hints are another method of content negotiation, which means changing content responses based on browser request headers.
One example of content negotiation involves the
Accept
request header. It describes what content types the browser understands, which
the server can use to negotiate the response. For image requests, the content
of Chrome’s Accept header is:
Accept: image/webp,image/apng,image/*,*/*;q=0.8
While all browsers support image formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF, Accept tells in this case that the browser also supports WebP and APNG. Using this information, we can negotiate the best image types for each browser:
<?php
// Check Accept for an "image/webp" substring.
$webp = stristr($_SERVER["HTTP_ACCEPT"], "image/webp") !== false ? true : false;
// Set the image URL based on the browser's WebP support status.
$imageFile = $webp ? "whats-up.webp" : "whats-up.jpg";
?>
<img src="<?php echo($imageFile); ?>" alt="I'm an image!">
Like Accept, client hints are another avenue for negotiating content, but in
the context of device capabilities and network conditions. With client hints, we
can make server side performance decisions based on a user's individual
experience, such as deciding whether non-critical resources should be served to
users with poor network conditions. In this guide, we’ll describe all the
available hints and some ways you can use them to make content delivery more
accommodating to users.
Opting in
Unlike the Accept header, client hints don’t just magically appear (with the
exception of Save-Data, which we’ll discuss later). In the interest of keeping
request headers at a minimum, you’ll need to opt into which client hints you’ll
want to receive by sending an Accept-CH header when a user requests a
resource:
Accept-CH: Viewport-Width, Downlink
The value for Accept-CH is a comma-separated list of requested hints the site
will use in determining the results for subsequent resource request. When the
client reads this header, it’s being told “this site wants the Viewport-Width
and Downlink client hints.” Don’t worry about the specific hints themselves.
We’ll get to those in a moment.
You can set these opt-in headers in any back-end language. For example, PHP’s
header function could be used.
You could even set these opt-in headers with the http-equiv
attribute
on a <meta> tag:
<meta http-equiv="Accept-CH" content="Viewport-Width, Downlink" />
All the client hints!
Client hints describe one of two things: the device your users, well, use, and the network they’re using to access your site. Let’s briefly cover all of the hints that are available.
Device hints
Some client hints describe characteristics of the user’s device, usually screen characteristics. Some of them can help you choose the optimal media resource for a given user’s screen, but not all of them are necessarily media-centric.
Before we get into this list, it might be helpful to learn a few key terms used to describe screens and media resolution:
Intrinsic size: the actual dimensions of a media resource. For example, if you open an image in Photoshop, the dimensions shown in the image size dialogue describe its intrinsic size.
Density-corrected intrinsic size: the dimensions of a media resource after it has been corrected for pixel density. It’s the image’s intrinsic size divided by a device pixel ratio. For example, let’s take this markup:
<img
src="whats-up-1x.png"
srcset="whats-up-2x.png 2x, whats-up-1x.png 1x"
alt="I'm that image you wanted."
/>
Let’s say the intrinsic size of the 1x image in this case is 320x240, and the
2x image’s intrinsic size is 640x480. If this markup is parsed by a client
installed on a device with a screen device pixel ratio of 2 (e.g., a Retina
screen), the 2x image is requested. The density-corrected intrinsic size of
the 2x image is 320x240, since 640x480 divided by 2 is 320x240.
Extrinsic size: the size of a media resource after CSS and other layout
factors (such as width and height attributes) have been applied to it. Let’s
say you have an <img> element that loads an image with a density-corrected
intrinsic size of 320x240, but it also has CSS width and height properties
with values of 256px and 192px applied to it, respectively. In this example,
the extrinsic size of that <img> element becomes 256x192.

width: 256px;
and height: 192px; transforms a 320x240 intrinsically sized image
to a 256x192 extrinsically sized one.With some terminology under our belt, let’s get into the list of device-specific client hints available to you.
Viewport-Width
Viewport-Width is the width of the user’s viewport in CSS pixels:
Viewport-Width: 320
This hint can used with other screen-specific hints to deliver different treatments (i.e., crops) of an image which are optimal for specific screen sizes (i.e., art direction), or to omit resources that are unnecessary for the current screen width.
DPR
DPR, short for device pixel ratio, reports the ratio of physical pixels to CSS
pixels of the user’s screen:
DPR: 2
This hint is useful when selecting image sources which correspond to a screen's
pixel density (like x descriptors do in the srcset
attribute).
Width
The Width hint appears on requests for image resources fired off by <img> or
<source> tags using the sizes
attribute.
sizes tells the browser what the extrinsic size of the resource will be;
Width uses that extrinsic size to request an image with an intrinsic size that
is optimal for the current layout.
For example, let’s say a user requests a page with a 320 CSS pixel wide screen
with a DPR of 2. The device loads a document with an <img> element containing
a sizes attribute value of 85vw (i.e., 85% of the viewport width for all
screen sizes). If the Width hint has been opted-into, the client will send
this Width hint to the server with the request for the <img>’s src:
Width: 544
In this case, the client is hinting to the server that an optimal intrinsic width for the requested image would be 85% of the viewport width (272 pixels) multiplied by the screen’s DPR (2), which equals 544 pixels.
This hint is especially powerful because it not only takes into account the density-corrected width of the screen, but also reconciles this critical piece of information with the image’s extrinsic size within the layout. This gives servers the opportunity to negotiate image responses that are optimal for both the screen and the layout.
Content-DPR
While you already know that screens have a device pixel ratio, resources also
have their own pixel ratios. In the simplest resource selection use cases, pixel
ratios between devices and resources can be the same. But! In cases where both
the DPR and Width headers are in play, the extrinsic size of a resource can
produce scenarios where the two differ. This is where the Content-DPR hint
comes into play.
Unlike other client hints, Content-DPR is not a request header to be used by
servers, but rather a response header servers must send whenever DPR and
Width hints are used to select a resource. The value of Content-DPR should
be the result of this equation:
Content-DPR = [Selected image resource size] / ([Width] / [DPR])
When a Content-DPR request header is sent, the browser will know how to scale
the given image for the screen’s device pixel ratio and the layout. Without it,
images may not scale properly.
Device-Memory
Technically a part of the Device Memory
API, Device-Memory reveals the
approximate amount of
memory
the current device has in GiB:
Device-Memory: 2
A possible use case for this hint would be to reduce the amount of JavaScript sent to browsers on devices with limited memory, as JavaScript is the most resource-intensive content type browsers typically load. Or you could send lower DPR images as they use less memory to decode.
Network hints
The Network Information API provides another category of client hints that describe the performance of the user’s network connection. In my opinion, these are the most useful set of hints. With them, we have the ability to tailor experiences to users by changing how we deliver resources to clients on slow connections.
RTT
The RTT hint provides the approximate Round Trip Time, in milliseconds, on
the application layer. The RTT hint, unlike transport layer RTT, includes
server processing time.
RTT: 125
This hint is useful because of the role latency plays in loading performance.
Using the RTT hint, we can make decisions based on network responsiveness,
which can help speed the delivery of an entire experience (e.g., through
omitting some requests).
Downlink
While latency is important in loading performance, bandwidth is influential,
too. The Downlink hint, expressed in megabits per second (Mbps), reveals the
approximate downstream speed of the user’s connection:
Downlink: 2.5
In conjunction with RTT, Downlink can be useful in changing how content is
delivered to users based on the quality of a network connection.
ECT
The ECT hint stands for Effective Connection Type. Its value is one of an
enumerated list of connection types, each of which describes a connection
within specified ranges of both RTT and Downlink
values.
This header doesn’t explain what the actual connection type is—for
example, it doesn’t report whether your gateway is a cell tower or a wifi access
point. Rather, it analyzes the current connection’s latency and bandwidth and
determines what network profile it resembles most. For example, if you connect
through wifi to a slow network, ECT may be populated with a value of 2g,
which is the closest approximation of the effective connection:
ECT: 2g
Valid values for ECT are 4g, 3g, 2g, and slow-2g. This hint can be
used as a starting point for assessing connection quality, and subsequently
refined using the RTT and Downlink hints.
Save-Data
Save-Data isn’t so much a hint describing network conditions as it is a user
preference stating that pages should send less data.
I prefer to classify Save-Data as a network hint because many of the things
you would do with it are similar to other network hints. Users may also be
likely to enable it in high latency/low bandwidth environments. This hint, when
present, always looks like this:
Save-Data: on
Here at Google, we’ve talked about what you can do with
Save-Data.
The impact it can have on performance can be profound. It’s a signal where users
are literally asking you to send them less stuff! If you listen and act on that
signal, users will appreciate it.
Tying it all together
What you do with client hints depends on you. Because they offer so much information, you have many options. To get some ideas flowing, let’s see what client hints can do for Sconnie Timber, a fictional timber company located in the rural Upper Midwest. As is often the case in remote areas, network connections can be fragile. This is where a technology like client hints can really make a difference for users.
Responsive Images
All but the simplest responsive image use cases can get complicated. What if you
have multiple treatments and variants of the same images for different screen
sizes—and different formats? That markup gets very complicated very
quickly.
It’s easy to get it wrong, and easy to forget or misunderstand important
concepts (such as sizes).
While <picture> and srcset are undeniably awesome tools, they can be
time-consuming to develop and maintain for complex use cases. We can automate
markup generation, but doing so is also difficult because the functionality
<picture> and srcset provides is complex enough that their automation needs
to be done in a way that maintains the flexibility they provide.
Client hints are can simplify this. Negotiating image responses with client hints could look something like this:
- If applicable to your workflow, first select an image treatment (i.e.,
art-directed imagery) by checking the
Viewport-Widthhint. - Select an image resolution by checking the
Widthhint and theDPRhint, and choosing a source that fits the image’s layout size and screen density (similar to howxandwdescriptors work insrcset). - Select the most optimal file format the browser supports (something
Accepthelps us do in most browsers).
Where my fictitious timber company client was concerned, I developed a naïve responsive image selection routine in PHP that uses client hints. This meant instead of sending this markup to all users:
<picture>
<source
srcset="
company-photo-256w.webp 256w,
company-photo-512w.webp 512w,
company-photo-768w.webp 768w,
company-photo-1024w.webp 1024w,
company-photo-1280w.webp 1280w
"
type="image/webp"
/>
<img
srcset="
company-photo-256w.jpg 256w,
company-photo-512w.jpg 512w,
company-photo-768w.jpg 768w,
company-photo-1024w.jpg 1024w,
company-photo-1280w.jpg 1280w
"
src="company-photo-256w.jpg"
sizes="(min-width: 560px) 251px, 88.43vw"
alt="The Sconnie Timber Staff!"
/>
</picture>
I was able to reduce it to the following based on individual browser support:
<img
src="/image/sizes:true/company-photo.jpg"
sizes="(min-width: 560px) 251px, 88.43vw"
alt="SAY CHEESY PICKLES."
/>
In this example, the /image URL is a PHP script followed by parameters
rewritten by
mod_rewrite. It
takes an image filename and additional parameters to help a back-end script
choose the best image in the given conditions.
I sense “But isn’t this just reimplementing <picture> and srcset on the
back-end?” is your first question.
In a way, yes—but with an important distinction: when an application uses client hints to craft media responses, most (if not all) of the work is much easier to automate, which can include a service (such as a CDN) that can do this on your behalf. Whereas with HTML solutions, new markup needs to be written to provide for every use case. Sure, you can automate markup generation. If your design or requirements change, though, there’s a good chance you’ll need to revisit your automation strategy in the future.
Client hints make it possible to start with a lossless, high-resolution
image that can then be dynamically resized to be optimal for any combination
of screen and layout. Unlike srcset, which requires you to enumerate a fixed
list of possible image candidates for the browser to choose from, this approach
can be more flexible. While srcset forces you to offer browsers a coarse set
of variants—say, 256w, 512w, 768w, and 1024w—a client-hints
powered solution can serve all widths, without a giant pile of markup.
Of course, you don’t have to write image selection logic yourself. Cloudinary
uses client hints to craft image responses when you use the w_auto
parameter,
and observed that median users downloaded 42% less bytes when using browsers
supporting client hints.
But beware! Changes in the desktop version of Chrome 67 have removed support for cross-origin client hints. Fortunately, these restrictions don’t affect mobile versions of Chrome, and they'll be lifted altogether for all platforms when work on Feature Policy is complete.
Helping users on slow networks
Adaptive performance is the idea that we can adjust how we deliver resources based on the information client hints makes available to us; specifically information surrounding the current state of the user’s network connection.
Where Sconnie Timber’s site is concerned, we take steps to lighten the load when
networks are slow, with Save-Data, ECT, RTT, and Downlink headers being
examined in our back-end code. When this is done, we generate a network quality
score we can use to determine if we should intervene for a better user
experience. This network score is between 0 and 1, where 0 is the worst
network possible network quality, and 1 is the best.
Initially, we check if Save-Data is present. If it is, the score is set to
0, as we’re assuming the user wants us to do whatever is necessary to make the
experience lighter and faster.
If Save-Data is absent, however, we move on and weigh the values of the ECT,
RTT, and Downlink hints to calculate a score that describes network
connection quality. The network score generation source
code
is available on Github. The takeaway is, if we use the network-related hints in
some fashion, we can make experiences better for those who are on slow
networks.
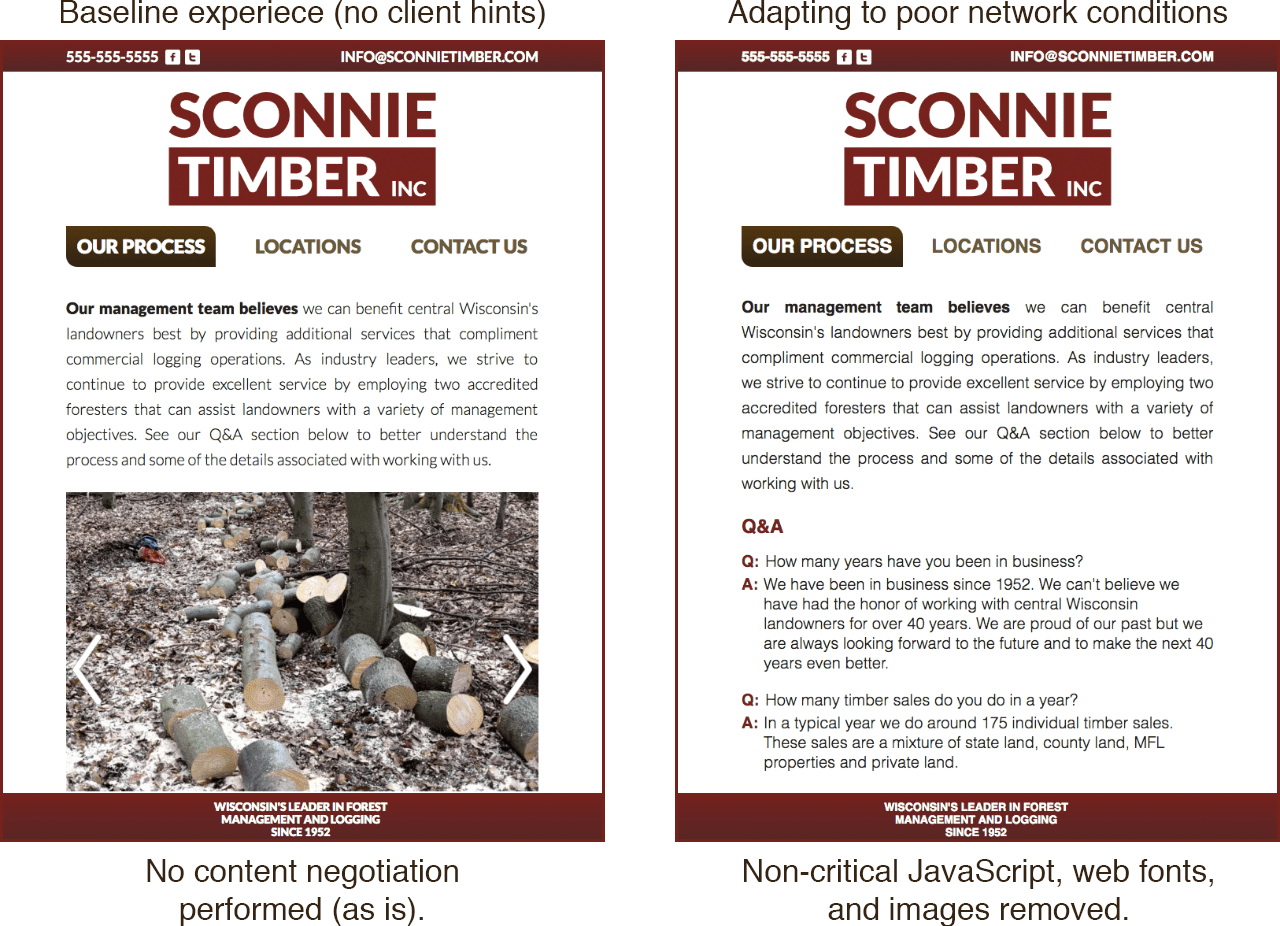
When sites adapt to the information client hints provide, we don’t have to adopt an “all or nothing” approach. We can intelligently decide which resources to send. We can modify our responsive image selection logic to send lower quality images for a given display to speed up loading performance when network quality is poor.
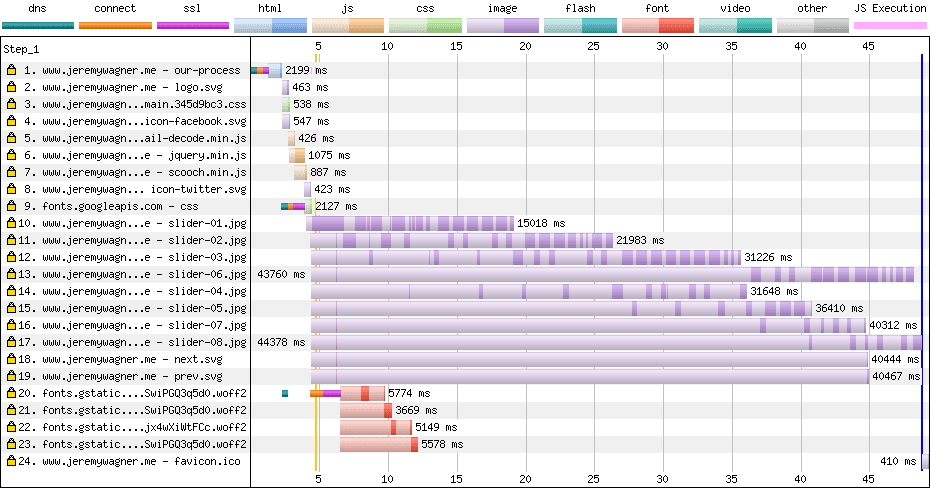
In this example, we can see the impact client hints have when it comes to improving the performance of sites on slower networks. Below is a WebPagetest waterfall of a site on a slow network that doesn’t adapt to client hints:
And now a waterfall for the same site on the same slow connection, except this time, the site uses client hints to eliminate non-critical page resources:
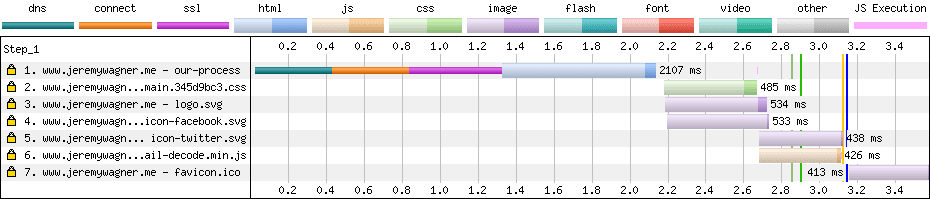
Client hints reduced the page load time from over 45 seconds to less than a tenth of that time. The benefits of client hints in this scenario can’t be emphasized enough and can be a serious boon to users seeking critical information over slow networks.
Furthermore, it’s possible to use client hints without breaking the experience
for browsers that don’t support them. For example, if we want adjust resource
delivery suing the value of the ECT hint while still delivering the full
experience for non-supporting browsers, we can set fall back to a default value
like so:
// Set the ECT value to "4g" by default.
$ect = isset($_SERVER["HTTP_ECT"]) ? $_SERVER["HTTP_ECT"] : "4g";
Here, "4g" represents the highest quality network connection the ECT header
describes. If we initialize $ect to "4g", browsers that don’t support client
hints won’t be affected. Opt-in FTW!
Mind those caches!
Whenever you change a response based on an HTTP header, you need to be aware of
how caches will handle future fetches for that resource. The Vary
header is
indispensable here, as it keys cache entries to the value of the request headers
supplied to it. Simply put, if you modify any response based on a given HTTP
request header, you should almost always include request that header in Vary
like so:
Vary: DPR, Width
There’s a big caveat to this, though: You never want to Vary cacheable
responses on a frequently changing header (like Cookie) because those
resources become effectively uncacheable. Knowing this, you might want to avoid
Varying on client hint headers such as RTT or Downlink, because those are
connection factors that could change quite often. If you want to modify
responses on those headers, consider keying only the ECT header, which will
minimize cache misses.
Of course, this only applies if you’re caching a response in the first place.
For example, you won’t cache HTML assets if their content is dynamic, because
that can break the user experience on repeat visits. In cases like these, feel
free to modify such responses on whatever basis you feel is necessary and not
concern yourself with Vary.
Client hints in service workers
Content negotiation isn’t just for servers anymore! Because service workers act
as proxies between clients and the servers, you have control over how resources
are delivered via JavaScript. This includes client hints. In the service worker
fetch event, you can use the event object’s
request.headers.get
method to read a resource’s request headers like so:
self.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
let dpr = event.request.headers.get('DPR');
let viewportWidth = event.request.headers.get('Viewport-Width');
let width = event.request.headers.get('Width');
event.respondWith(
(async function () {
// Do what you will with these hints!
})(),
);
});
Any client hint header you opt into can be read in this fashion. Though that’s
not the only way you can get some of this information. Network-specific hints
can be read in these equivalent JavaScript properties in the navigator object:
| Client hint | JS equivalent |
|---|---|
| `ECT` | `navigator.connection.effectiveType` |
| `RTT` | `navigator.connection.rtt` |
| `Save-Data` | `navigator.connection.saveData` |
| `Downlink` | `navigator.connection.downlink` |
| `Device-Memory` | `navigator.deviceMemory` |
Because these APIs aren’t available everywhere you need feature check with the
in
operator:
if ('connection' in navigator) {
// Work with netinfo API properties in JavaScript!
}
From here, you can use logic similar to what you would use on the server, except you don’t need a server to negotiate content with client hints. Service workers alone have the power to make experiences faster and more resilient due to the added ability they have to serve content when the user is offline.
Wrapping up
With client hints, we have the power to make experiences faster for users in a
fully progressive way. We can serve media based on the user’s device
capabilities in a way that makes serving responsive images easier than relying
on <picture> and srcset, especially for complex use cases. This enables us
to not only reduce time and effort on the development side, but also to optimize
resources—particularly images—in a way that targets user’s screens
more finely than
Perhaps more importantly, we can sniff out poor network connections and bridge the gap for users by modifying what we send—and how we send it. This can go a long way in making sites easier to access for users on fragile networks. Combined with service workers, we can create incredibly fast sites that are available offline.
While client hints are only available in Chrome—and Chromium-based browsers—it’s possible to use them in such a way that doesn’t encumber browsers that don’t support them. Consider using client hints to create truly inclusive and adaptable experiences that are aware of every user’s device capabilities, and the networks they connect to. Hopefully, other browser vendors will see the value of them and show intent to implement.
Resources
- Automatic Responsive Images with Client Hints
- Client Hints and Responsive Images—What Changed in Chrome 67
- Take a (Client) Hint! (Slides)
- Delivering Fast and Light Applications with
Save-Data
Thank you to Ilya Grigorik, Eric Portis, Jeff Posnick, Yoav Weiss, and Estelle Weyl for their valuable feedback and edits on this article.

